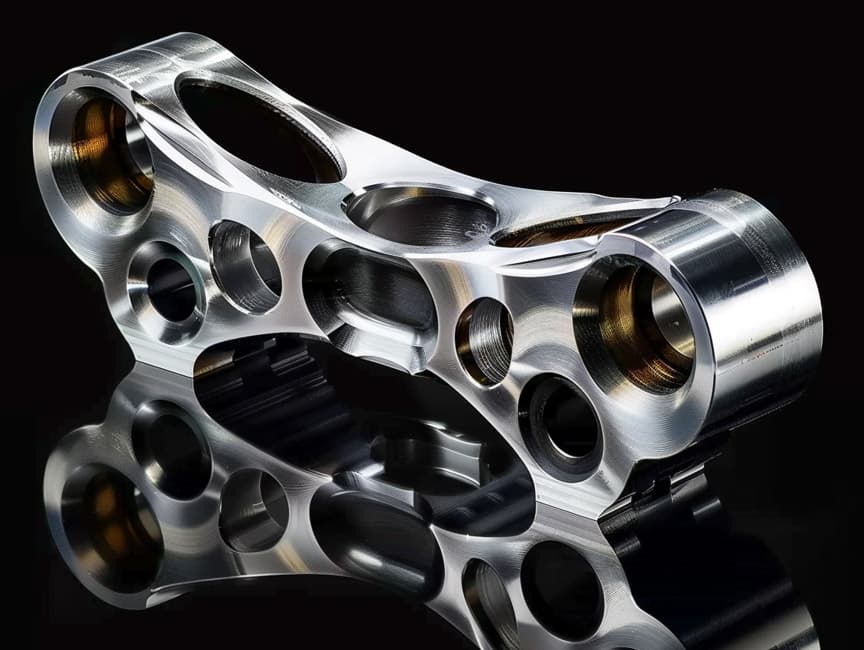
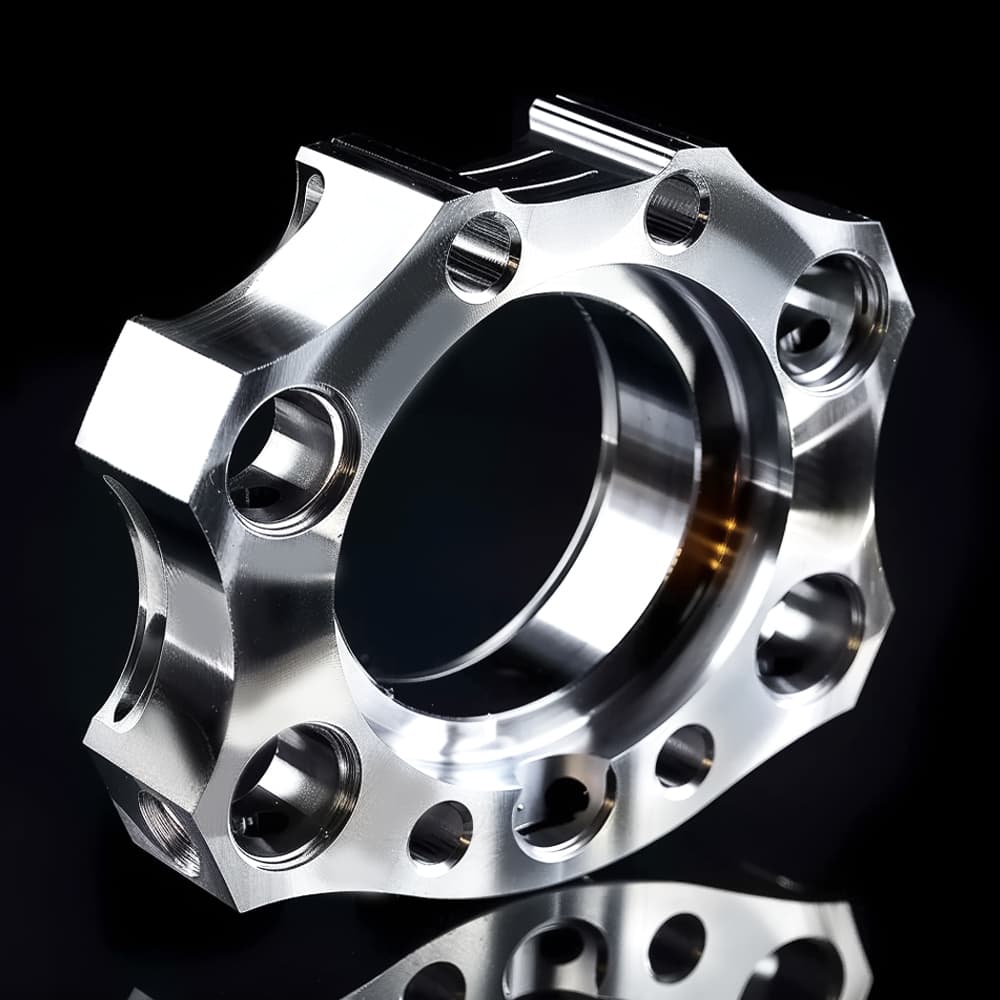
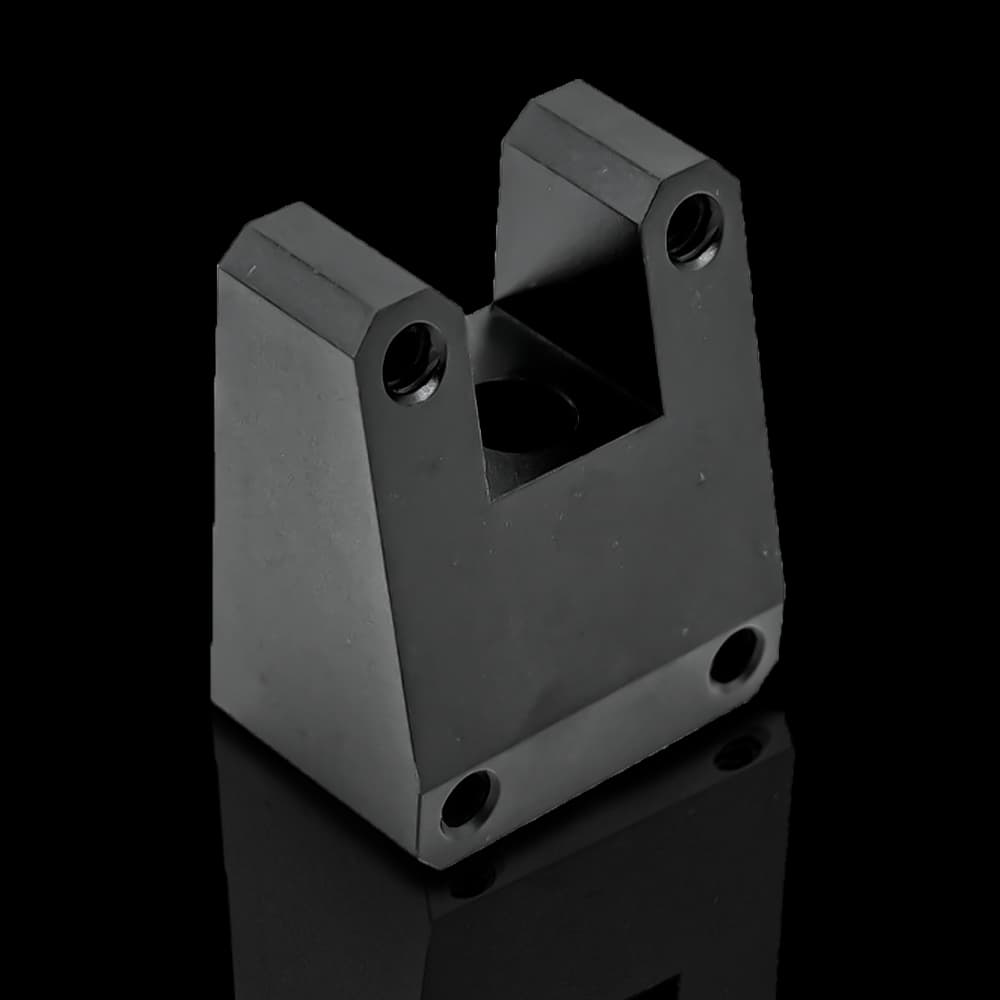
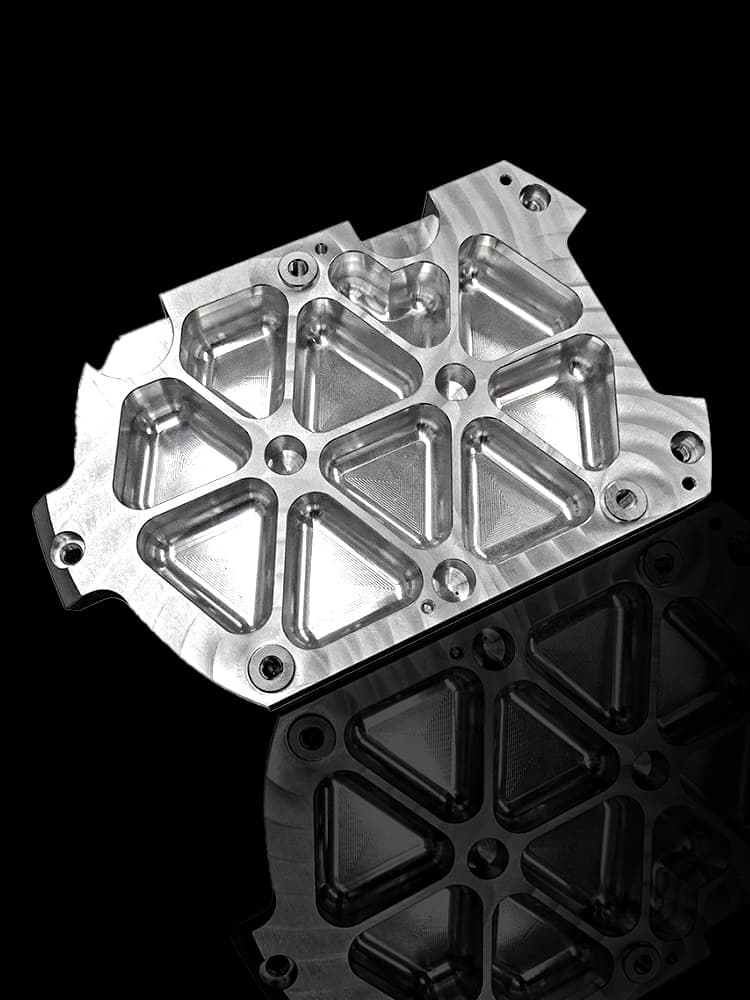
Custom-Made CNC Titanium Parts Precision Machining to Your Specifications!
All uploads are secure and confidential. Learn more.

IOS 9001
IOS 14001

Classification of Titanium Alloys by Composition
Commercially Pure Titanium: Pure titanium that does not contain other alloying elements, primarily composed of titanium.
Titanium Alloy: Contains other alloying elements in addition to titanium, such as aluminum, vanadium, tin, zirconium, iron, etc., to enhance its properties or suit specific application requirements.
| Type | Model | Material Properties | Application Industries | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Commercially Pure Titanium | TA1 (GB Standard) | Pure titanium, lowest strength, highest ductility, excellent corrosion resistance | Chemical, Marine Equipment, Medical Devices | ||
| TA2 (GB Standard) | Pure titanium, medium strength, good toughness and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, Industrial, Biomedical | |||
| TA3 (GB Standard) | Pure titanium, high strength, excellent wear resistance and corrosion resistance | Construction, Aerospace, Chemical | |||
| TA4 (GB Standard) | Pure titanium, the highest strength, good corrosion resistance and formability | Aerospace, Marine Exploration, High-Performance Applications | |||
| Titanium Alloy | Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) | High strength, good toughness and corrosion resistance, weldable | Aerospace, Automotive, Biomedical, Sports Equipment | ||
| Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) | Low impurities, higher purity and toughness | Medical Implants, Aerospace, Chemical | |||
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo (Ti-6246) | High strength, excellent high-temperature performance and creep resistance | Aerospace Engines, Military Applications | |||
| Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al (Ti-10-2-3) | Extremely high strength and fatigue resistance, excellent formability | Aerospace, Sports Equipment, High-Performance Engineering Components | |||
List of Titanium and Titanium Alloy Materials
| Type | Model | Material Properties | Application Industries | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure Titanium | Grade 1 | Softest, good ductility, weldability, corrosion resistance | Chemical, Marine, Aerospace | ||
| Pure Titanium | Grade 2 | Good strength, ductility, and weldability | Chemical, Marine, Aerospace, Biomedical | ||
| Pure Titanium | Grade 3 | High strength, good corrosion resistance, and weldability | Extracorporeal Orthopedic Applications, Aerospace, Chemical | ||
| Pure Titanium | Grade 4 | Strongest commercial pure titanium, good corrosion resistance, and weldability | Aerospace, Chemical, Biomedical | ||
| α Alloy | Ti 5Al-2.5Sn | Good corrosion resistance, high toughness, high-temperature resistance | Aerospace, Military, Marine | ||
| α Alloy | Ti 8Al-1Mo-1V | High strength, good corrosion resistance, and creep resistance | Aerospace Engine Components | ||
| Near α Alloy | Ti 6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo | Good corrosion resistance, creep resistance, and fracture toughness | Aerospace Engine Components | ||
| α-β Alloy | Ti-6Al-4V (Grade 5) | Most commonly used, excellent strength, toughness, and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, Biomedical, Automotive, Industrial | ||
| α-β Alloy | Ti-6Al-4V ELI | Low oxygen version, higher purity and toughness | Medical Implants, Aerospace | ||
| β Alloy | Ti 15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al | High strength, superior formability, and outstanding corrosion resistance | Aerospace, Sports Equipment | ||
| β Alloy | Ti 10V-2Fe-3Al | Very high strength and fatigue resistance, can significantly enhance properties through heat treatment | Aerospace, Sports Equipment | ||
| Special Alloy | Ti-5.5Al-3.5Sn-3Zr-1Nb-0.25Mo-0.7Si | High strength, high-temperature, and creep resistance | High-Temperature Aerospace Applications | ||
Titanium Surface Treatment

Plating

Blackening
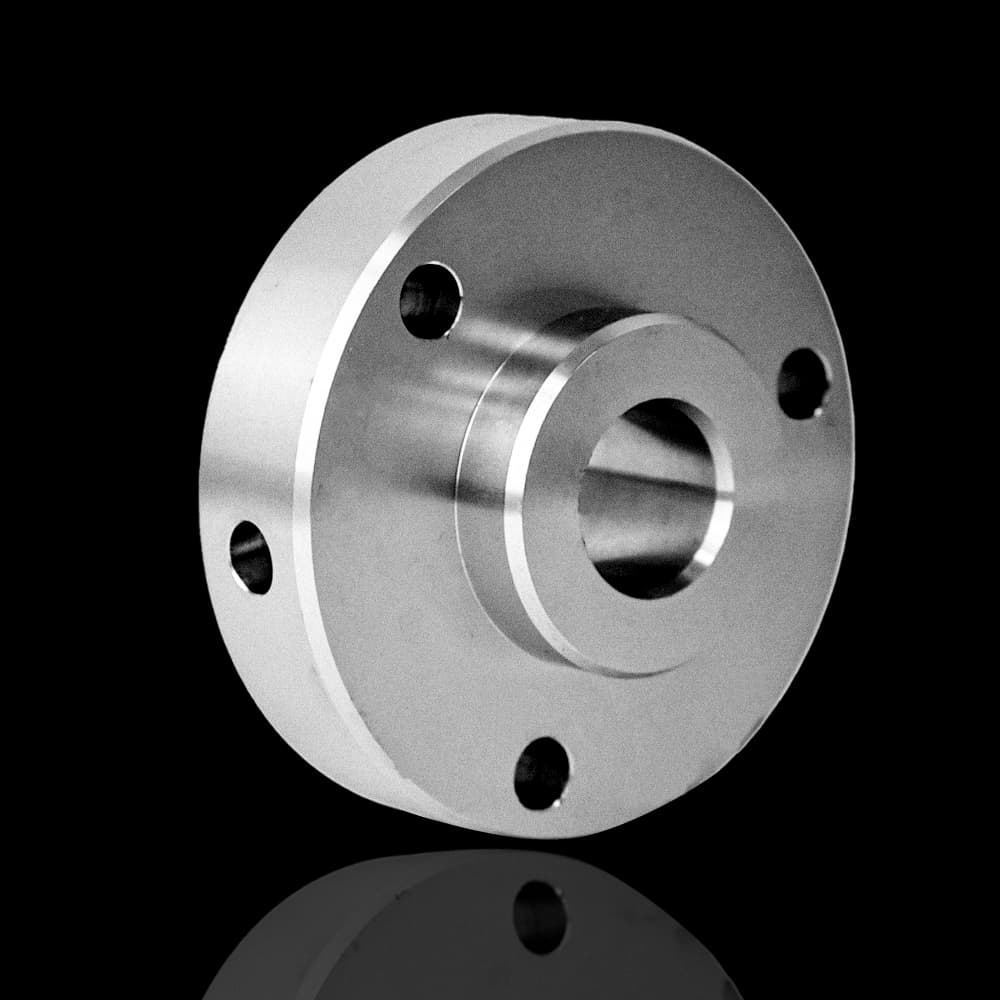

Sandblasted
| Type | Surface Treatment | Surface Effect | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bead Blasting | A cold working process where small spherical media bombard the part surface to improve fatigue life | No texture | ||
| Sandblasted | Using compressed air to propel sand onto the surface for cleaning or grinding | Can be matte, semi-gloss, or glossy, usually no specific color | ||
| Hardcoat anodizing | Forming a thick, hard protective oxide layer on the surface to enhance wear resistance and corrosion resistance | Black, gray | ||
| Black Oxide | Creating a blackened conversion coating that provides corrosion resistance | Black | ||
| Phosphating | A chemical conversion coating process used to improve the corrosion resistance of steel surfaces and promote paint adhesion | Gray | ||
| Passivation | Removing iron from the metal surface to enhance corrosion resistance | Smooth surface | ||
| Electrophoretic | Coating the metal surface with an organic or inorganic layer to provide decorative effects and corrosion resistance | Various (including black, white, red, green, champagne, blue) | ||
| Electroplating | Depositing a thin layer of metal on the substrate to provide corrosion resistance and decorative effects | Various (depending on plating material) | ||
| Electropolishing | Removing surface material to produce a smooth, shiny surface | Mirror-like | ||
| Nickel Plating | Depositing nickel onto the metal surface to provide decorative effects and corrosion resistance | Silver | ||
| Tin Plating | Depositing tin onto the metal surface to provide decorative effects and corrosion resistance | Silver | ||
| PVD | Depositing thin films of metal, metal compounds, or ceramics on the surface to enhance hardness, corrosion resistance, and aesthetics | Various colors | ||
| DLC Coating | Depositing a carbon material film with diamond-like properties onto the surface to enhance hardness and wear resistance | Black | ||
| Titanium Nitride Coating | Depositing a layer of titanium nitride to enhance hardness and wear resistance | Gold, black | ||
| Chromium Nitride Coating | Depositing a layer of chromium nitride to enhance hardness and wear resistance | Silver | ||
| Powder Coating | Spraying fine powders of pigments and resins onto the surface to form a uniform coating, providing corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and decorative effects | Various colors (depending on powder color) | ||
| Painting | Applying liquid paint to the surface to provide protection and decoration | Various (depending on paint color) | ||
| Heat Treatment | Controlling heating and cooling processes to alter the physical and mechanical properties of the material | No change | ||
| Laser Marking | Using a laser beam to make high-precision markings or engravings on the surface | Various (depending on material) | ||
| Cleaning | Removing grease, oil, and other contaminants from the surface | No change | ||
CNC Titanium Parts Case Study
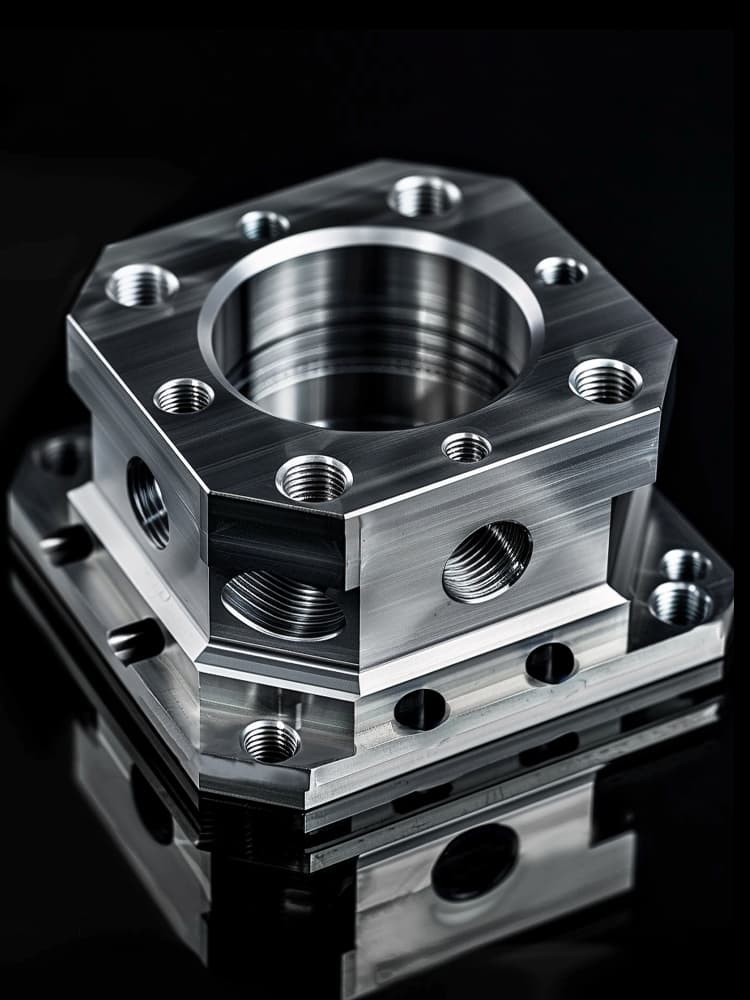
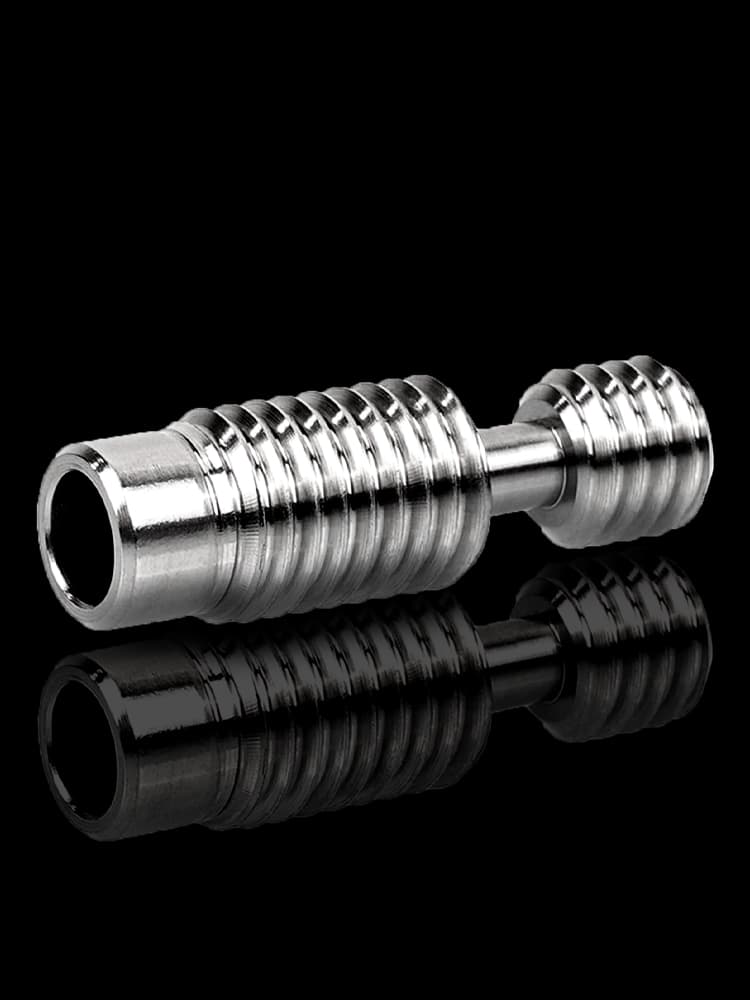
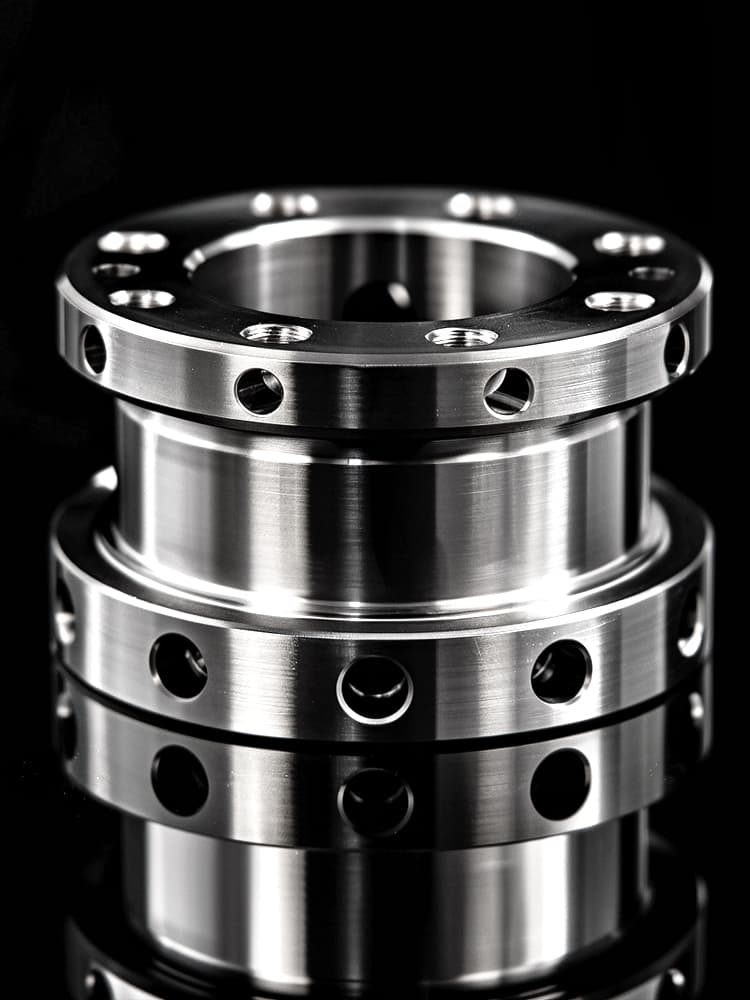
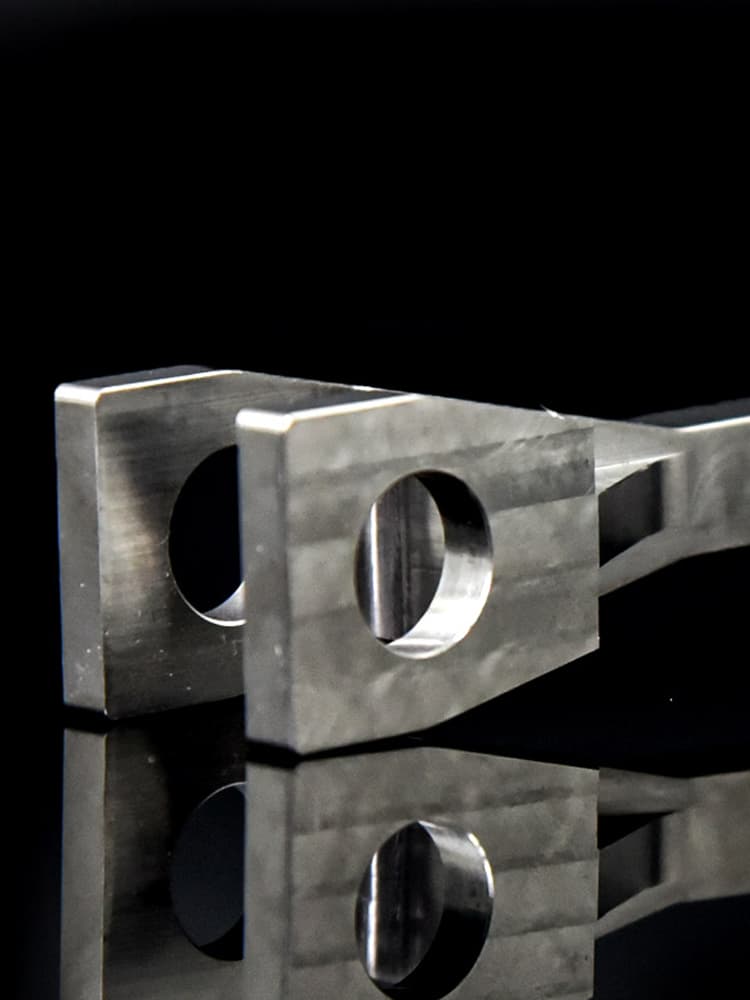
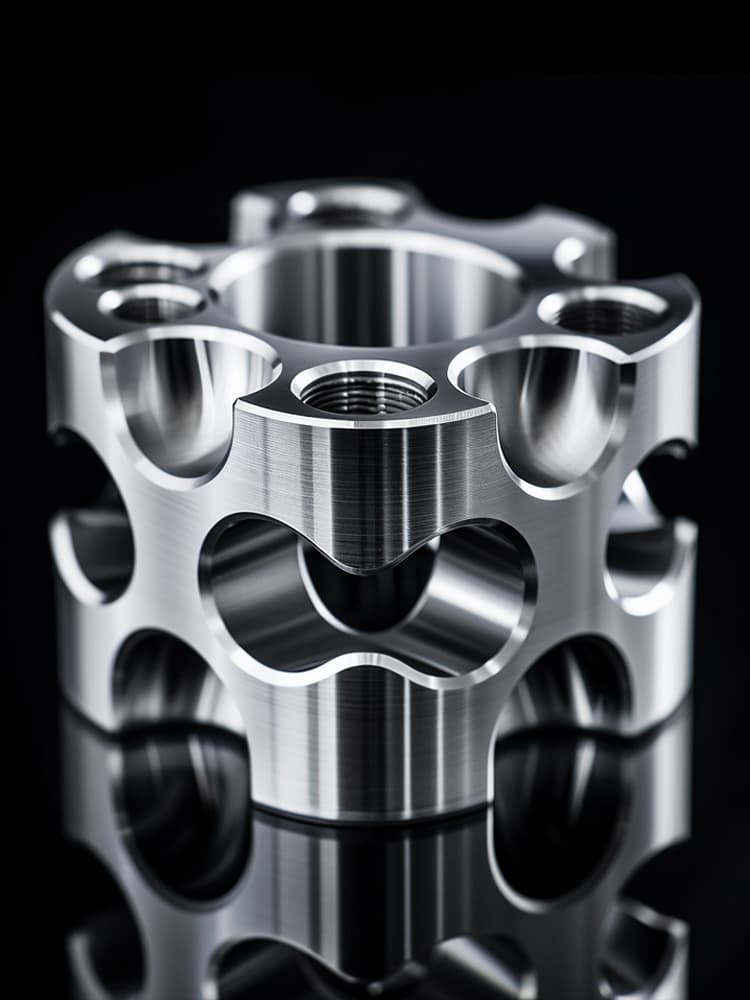
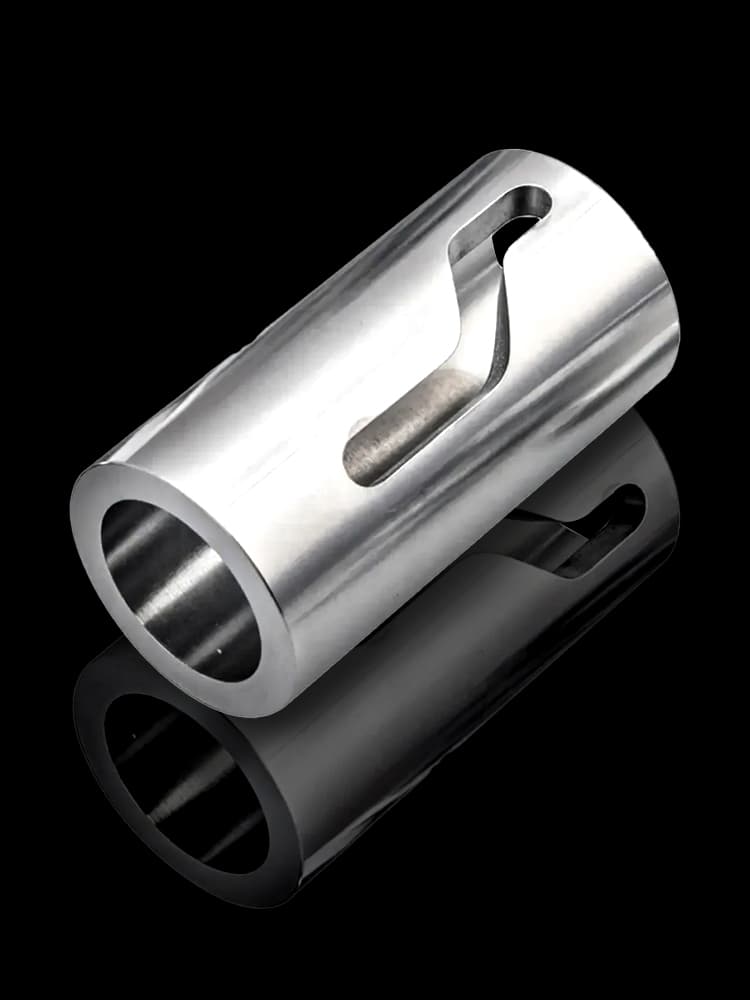
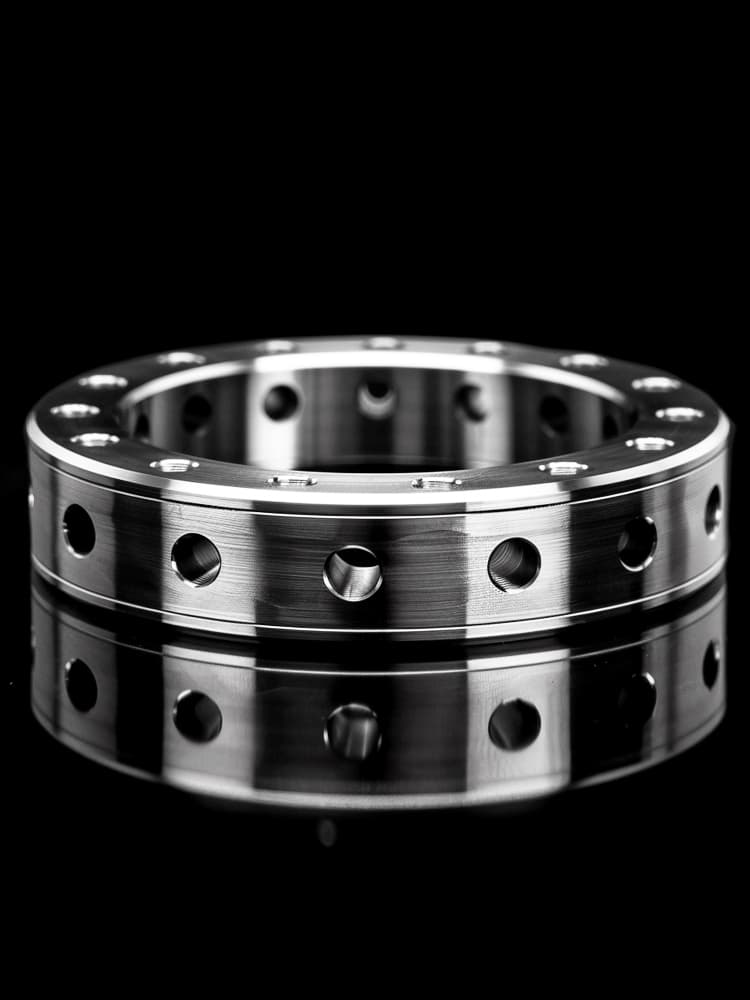
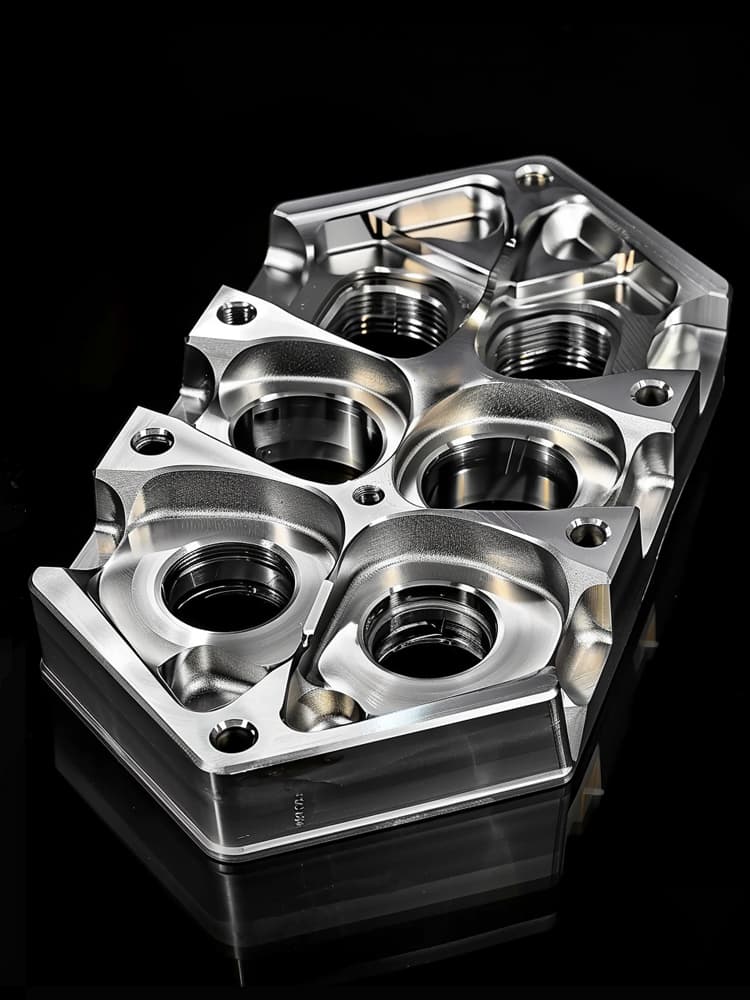
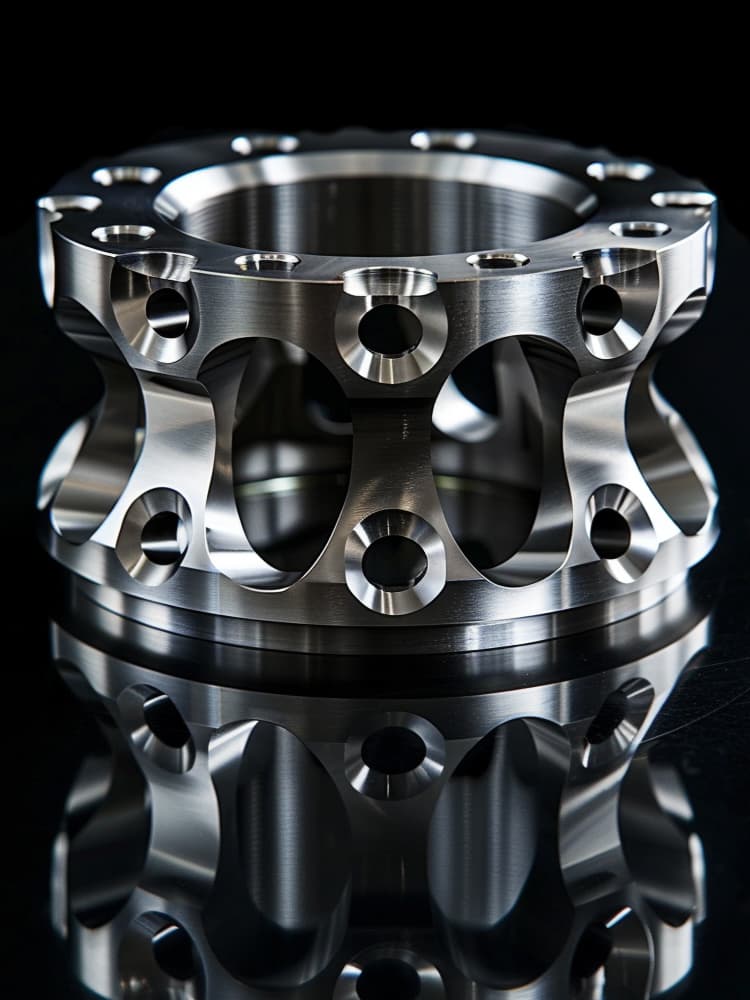
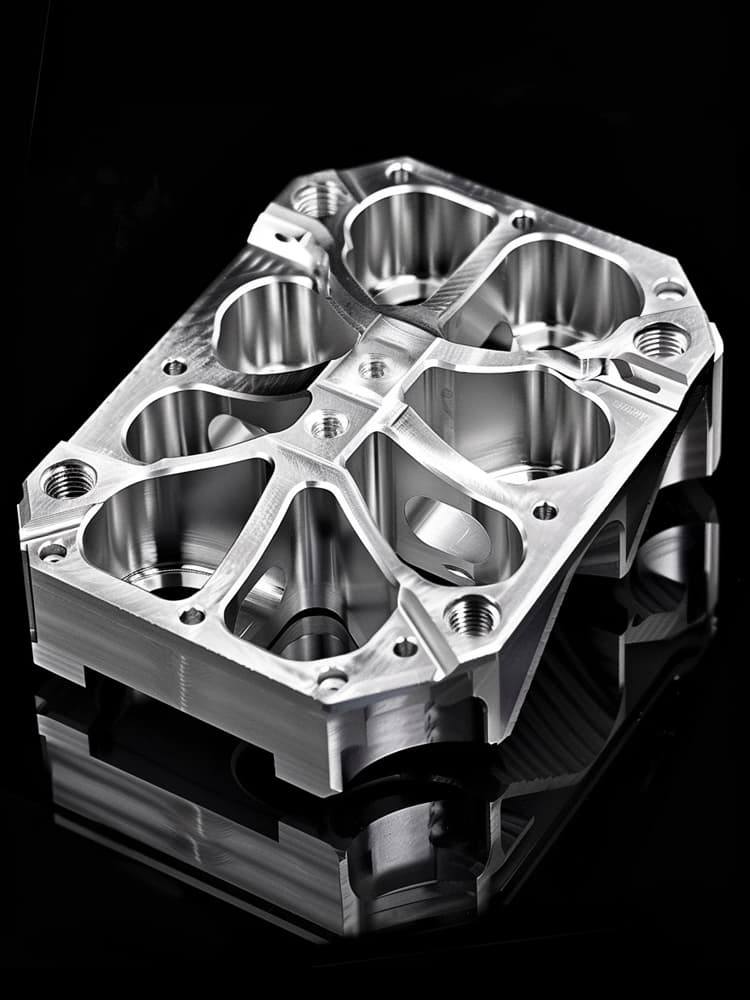










Selection Guide
Classification of Titanium Alloys by Application Area
Titanium alloys offer high strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability for aerospace; biocompatibility for medical implants and devices; and are used in industrial applications like chemical equipment and shipbuilding.
| Application Area | Model | Material Properties | Application Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) | Excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability | Aerospace, aircraft engine manufacturing, etc. |
| Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo (Ti-6246) | High strength, excellent high-temperature performance, and creep resistance | Aerospace | |
| Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al (Ti-10-2-3) | Excellent high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, aircraft engine manufacturing, etc. | |
| Medical | Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) | Low impurities, higher purity, and toughness | Medical devices, orthopedic implants, artificial joints, etc. |
| Ti-6Al-7Nb (TAVNS) | Good biocompatibility | Medical devices, orthopedic implants, artificial joints, etc. | |
| Industrial | Ti-3Al-2.5V (Ti-3-2.5) | High toughness and good corrosion resistance, high fatigue resistance | Chemical equipment, marine engineering, shipbuilding, etc. |
| Ti-6Al-4V (TC4) | Excellent corrosion resistance and strength, high mechanical performance | Chemical equipment, marine engineering, shipbuilding, etc. | |
| Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Extra Low Interstitial) | High strength, corrosion resistance, excellent welding, and machining properties | Chemical equipment, marine engineering, shipbuilding, etc. |
Classification of Titanium Alloys by Performance
Titanium alloys are classified based on performance characteristics, which are typically related to the alloy’s chemical composition and heat treatment processes. The categories include: High-Strength, High-Toughness, High-Corrosion-Resistance and High-Temperature Alloys.
| Types of Titanium Alloys | Model | Material Properties | Application Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-Strength Titanium Alloys | Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al | High strength, good toughness, and weldability | Aerospace, military, sports equipment |
| Ti-6Al-4V | High strength, good toughness, and corrosion resistance | Aerospace, medical devices, high-performance engineering | |
| High-Toughness Titanium Alloys | Ti 5Al-2.5Sn | Excellent fracture resistance and good low-temperature performance | Aerospace, cold region engineering |
| Ti-8Al-1Mo-1V | High toughness, excellent corrosion resistance, and high-temperature performance | Aerospace, military applications | |
| High-Corrosion-Resistance Titanium Alloys | Ti 2Al-2.5Zr | Excellent resistance to chemical and marine environment corrosion | Chemical equipment, marine applications |
| Ti 3Al-2.5V | Excellent corrosion resistance, suitable for welding and forming | Chemical, marine engineering, aerospace | |
| High-Temperature Titanium Alloys | Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-6Mo | Good mechanical properties and high-temperature performance | Aircraft engines, high-temperature industrial processes |
| Ti-5.5Al-3.5Sn-3Zr-1Nb-0.25Mo-0.7Si | Excellent high-temperature performance and strong creep resistance | Aircraft engine components, turbine blades |
Classification of Titanium Alloys by Structure
Titanium alloys can be classified into three types based on their crystal structure at room temperature:
α (Alpha) Titanium Alloys, β (Beta) Titanium Alloys, α-β (Alpha-beta) Titanium Alloys.
| Types of Titanium Alloys | Model | Typical Alloys | Structural Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| α (Alpha) Titanium Alloys | α(Alpha) | Ti 5Al-2.5Sn, Ti 8Al-1Mo-1V | Pure α phase, hexagonal close-packed structure (HCP) | Alpha (α) Alloys: Chemical, marine, and aerospace applications requiring good weldability, toughness, and corrosion resistance |
| β (Beta) Titanium Alloys | β(Beta) | Ti 15V-3Cr-3Sn-3Al, Ti 10V-2Fe-3Al | Pure β phase, body-centered cubic structure (BCC) | Beta (β) Alloys: Aerospace and sports equipment applications requiring high strength, excellent weldability, and formability |
| α-β (Alpha-beta) Titanium Alloys | α-β(Alpha-beta) | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6Al-6V-2Sn | Mixed α and β phases, this is the most common type of titanium alloy | Alpha-beta (α-β) Alloys: Aerospace, medical devices, automotive, and industrial applications requiring high strength and good corrosion resistance |
Xielifeng Order Process of CNC Titanium Parts
From quotation to delivery, we provide efficient and high-quality services, making manufacturing more convenient
01
Upload drawing
02
DFM Evaluation & Quote

03
Order Confirmtion & Production
04
Quality Inspection & Delivery