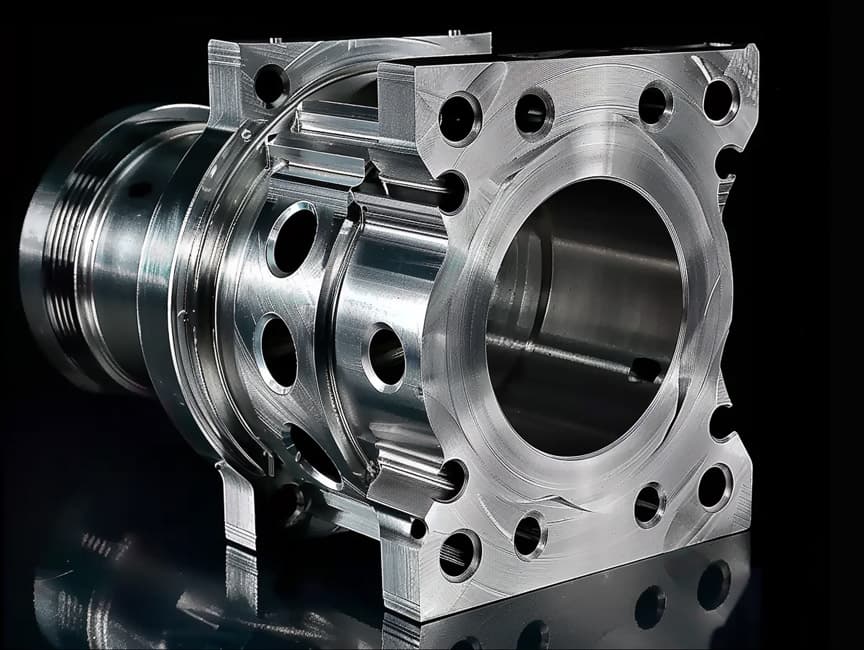
Steel CNC Machining
Extensive steel options for CNC machining, perfect for prototypes and custom end-use parts in various industries.
Stainless Steel
Carbon Steel
Alloy Steel
Tool Steel
All uploads are secure and confidential. Learn more.

ISO 9001
ISO 14001


Steel
Steel is widely used in manufacturing due to its excellent mechanical properties, including high strength, hardness, wear resistance, plasticity, and machinability. It is ideal for CNC machining parts like bearings, gears, molds, and dies in the automotive, aerospace, and machinery manufacturing industries.
Description
Application Industries: Automotive Manufacturing, Aerospace Industry, Machinery Manufacturing, Construction Industry, Energy Sector, etc.
Advantages: High strength, good plasticity and machinability, excellent wear resistance, wide variety of types and specifications.
Weaknesses: Heavy weight, susceptible to temperature effects.
Features
Price: $$$
Maximum Part Size:
236“ x 118” x 24“ (6,000×3,000 x 610 mm)
Delivery Time: 2-15 working days
Steel Selection Guide
Our team of skilled engineers is here to help you select the most suitable material for your project, ensuring optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and see how our machining expertise can bring your ideas to life.
| Steel Classification | Feature | Application | Price | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Carbon Steel | Easy to weld and process | Structural parts, general machinery | $ | ||||||||||
| Medium Carbon Steel | High strength and hardness | Transmission shafts, axles, mechanical parts | $$ | ||||||||||
| High Carbon Steel | High hardness and wear resistance, brittle | Tools, springs, bearings | $$ | ||||||||||
| Alloy Steel | High strength, toughness, suitable for heavy load applications | Automotive manufacturing, gears, bearings | $$ | ||||||||||
| Stainless Steel | High-Temperature resistance, good corrosion resistance | Food manufacturing, medical industry, household items | $$$ | ||||||||||
| Tool Steel | Good wear resistance and cutting performance | Machinery manufacturing, mold making, aerospace industry | $$$$ | ||||||||||
Stainles Steel Typical Materials
Strength: Resistance to deformation and failure; “High” means it withstands significant force without breaking.
Hardness: Resistance to scratches, indentations, and wear; “High” means better protection against physical impacts.
Mechanical Properties: Includes the material’s toughness, ductility, etc.
Machinability: Ease of cutting and performance during machining.
| Materials | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Hardness | Machinability | Application | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | Food Processing, Kitchenware, General Chemical Equipment | $$$ |
| 304F | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | Automated Turning, Precision Parts | $$$$ |
| 304L | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★ | ★★★ | Welding Structures, Chemical Processing Equipment | $$$ |
| 303 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | Precision Parts, Fasteners, Electronic Equipment | $$$ |
| 316 | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | Medical Equipment, Marine Environment Equipment | $$$$ |
| 316F | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | Precision Machinery Processing | $$$$ |
| 316L | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★ | ★★★ | Medical Equipment, Food Processing | $$$$ |
| 316Ti | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | High-Temperature Chemical Processing Equipment | $$$$ |
| 201 | ★★★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | Low-cost Consumer Goods | $$ |
| 310S | ★★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | High-Temperature Applications, Furnace Components | $$$$ |
| 440C | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Knives, Bearings | $$$$ |
| 410 | ★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★ | Pumps, Valves, Knives | $$ |
| 416 | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Gears, Shafts, Fasteners | $$$ |
| 420 | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Knives, Medical Instruments | $$$ |
| 440F | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Precision Parts, High Wear Applications | $$$$ |
| 440 | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Knives, Bearings | $$$$ |
| 430 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Household Appliances, Decorative Components | $$ |
| 630 | ★★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Aerospace Structures, Nuclear Reactor Components | $$$$ |
| 17-4 PH | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Aerospace, Chemical, Food Processing, Nuclear Industry | $$$$ |
| 13-8 Mo | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★★ | Aerospace Parts, Nuclear Facilities, Chemical Processing | $$$$ |
Carbon Steel Typical Materials
Corrosion Resistance: Measures the material’s ability to resist rust in various environments.
Strength: The material’s ability to resist deformation and failure.
Hardness: The material’s ability to resist permanent deformation (such as scratches and indentations).
Mechanical Properties: Includes the material’s toughness, ductility, etc.
Machinability: Describes how the material performs during machining, such as ease of cutting.
| Materials | Carbon Content (%) | Strength | Toughness | Plasticity | Weldability | Applications | Price | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1144 | 0.40-0.48 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★ | High-strength Bearings, Fasteners | $$ | |||||||
| Q235 | 0.17-0.22 | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Construction Steel, Bridges | $ | |||||||
| Q215 | 0.12-0.18 | ★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Light Structures, Furniture | $ | |||||||
| 1040 | 0.37-0.44 | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Mechanical Parts, Crankshafts | $$ | |||||||
| 1045 | 0.43-0.50 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Shafts, Gears, Crankshafts | $$ | |||||||
| 1018 | 0.15-0.20 | ★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Fasteners, Structural Steel | $ | |||||||
| 20#Steel | 0.17-0.24 | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Pipes, Small Bearings | $ | |||||||
| 35#Steel | 0.32-0.39 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Mechanical Structures, Small Gears | $$ | |||||||
| 45#Steel | 0.42-0.50 | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Molds, Bearings, Stamping Parts | $$ | |||||||
| 60#Steel | 0.57-0.65 | ★★★★ | ★ | ★ | ★ | Springs, High-strength Fasteners | $$ | |||||||
| Y40Mn | 0.37-0.45 | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Shafts, Gears, Tools | $$ | |||||||
| s20c | 0.18-0.23 | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Light Structures, Automotive Parts | $ | |||||||
| 11SMn30 | 0.09-0.14 | ★ | ★★ | ★★★ | ★ | Automatic Lathe Processing, Precision Parts | $$ | |||||||
| 1214 | 0.09-0.15 | ★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★ | Bolts, Fasteners, Free-cutting Parts | $ | |||||||
| 1215 | 0.09-0.15 | ★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | ★ | Fasteners, Free-cutting Parts, Furniture Parts | $ | |||||||
Alloy Steel Typical Materials
Corrosion Resistance: Reflects the material’s performance in corrosive environments.
Strength: Indicates the material’s ability to withstand tensile, compressive, and other forces.
Hardness: Indicates the material’s surface resistance to indentation.
Wear Resistance: The material’s ability to resist wear is related to hardness.
Machinability: Describes the ease of processing the material during mechanical machining.
| Materials | Composition | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Wear Resistance | Application | Price | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40Cr | Cr, Mn, Si, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Gears, Bearings, Automotive Parts | $ | ||||||||||
| 4140 | Cr, Mn, Mo, Si, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Shafts, Crankshafts, Gears, Molds | $ | ||||||||||
| 4130 | Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Aerospace, Race Car Parts | $ | ||||||||||
| 16MnCr5 | Mn, Cr, C | ★★ | ★★ | ★★ | Gears, Bearings, Vehicle Transmission Parts | $ | ||||||||||
| 30CrMo | Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Industrial Pressure Vessels, High-Strength Bolts | $ | ||||||||||
| 30CrMoV9 | Cr, Mo, V, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | High-Performance Gears and Shafts, Aerospace | $ | ||||||||||
| 38NiCrMo4 | Ni, Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Heavy Machinery, Engineering and Structural | $ | ||||||||||
| 42CrMo | Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★★★ | ★★★★ | High-Strength Bolts, Structural Parts, Crankshafts | $$ | ||||||||||
| EN24 | Ni, Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Bearings, Gears, Heavy Load Applications | $ | ||||||||||
| 4340 | Ni, Cr, Mo, C | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★★ | Aerospace, Automotive, Molds | $ | ||||||||||
| A514 T1 | Cr, Mo | ★ | ★★★★ | ★★★ | Construction, Bridges and Building Supports | $$ | ||||||||||
| Q345B | Fe, C, Mn, Si | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★ | Construction, Manufacturing, Ships, Vehicles | $ | ||||||||||
| Q345 | Fe, C, Mn, Si | ★★ | ★★★ | ★★ | Engineering Structures, Mechanical Parts, Vehicles | $ | ||||||||||
Tool Steel Typical Materials
| Material Name | Features | Disadvantages | Application | Price | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2 Tool Steel | High wear resistance and hardness, good dimensional stability | Difficult to machine, high tool wear | Stamping dies, cutting tools, long-life tools | $$$ | ||||||||||||||
| M2 High-Speed Steel | High wear resistance, good thermal stability, works at high temperatures | Relatively expensive, difficult to weld | Manufacturing drills, taps, cutting tools, and high-speed cutting tools | $$$$ | ||||||||||||||
| A2 Tool Steel | Good overall performance, including wear resistance and toughness | Moderate machinability, stringent heat treatment requirements | Stamping dies, mold components, precision machining tools | $$$ | ||||||||||||||
| S7 Tool Steel | High toughness, easy to machine | Wear resistance and hardness are lower compared to other tool steels | Stamping dies, punches, rivet sets, break dies | $$$ | ||||||||||||||
| O1 Tool Steel | Good wear resistance and stability, easy to heat treat | Relatively lower hardness, corrosion resistance not as good as stainless steel | Knives, dies, molds | $$ | ||||||||||||||
| P20 Tool Steel | Excellent machinability, can be used after pre-hardening | Low hardness, not suitable for high-temperature applications | Plastic injection molds, mold bases and TV frames | $$$ | ||||||||||||||
| H13 Tool Steel | High toughness and hardness, strong thermal fatigue resistance | Difficult to machine, stringent heat treatment requirements | High-temperature forging dies, extrusion dies, hot shear blades | $$$$ | ||||||||||||||
Steel Surface Treatment

Polished
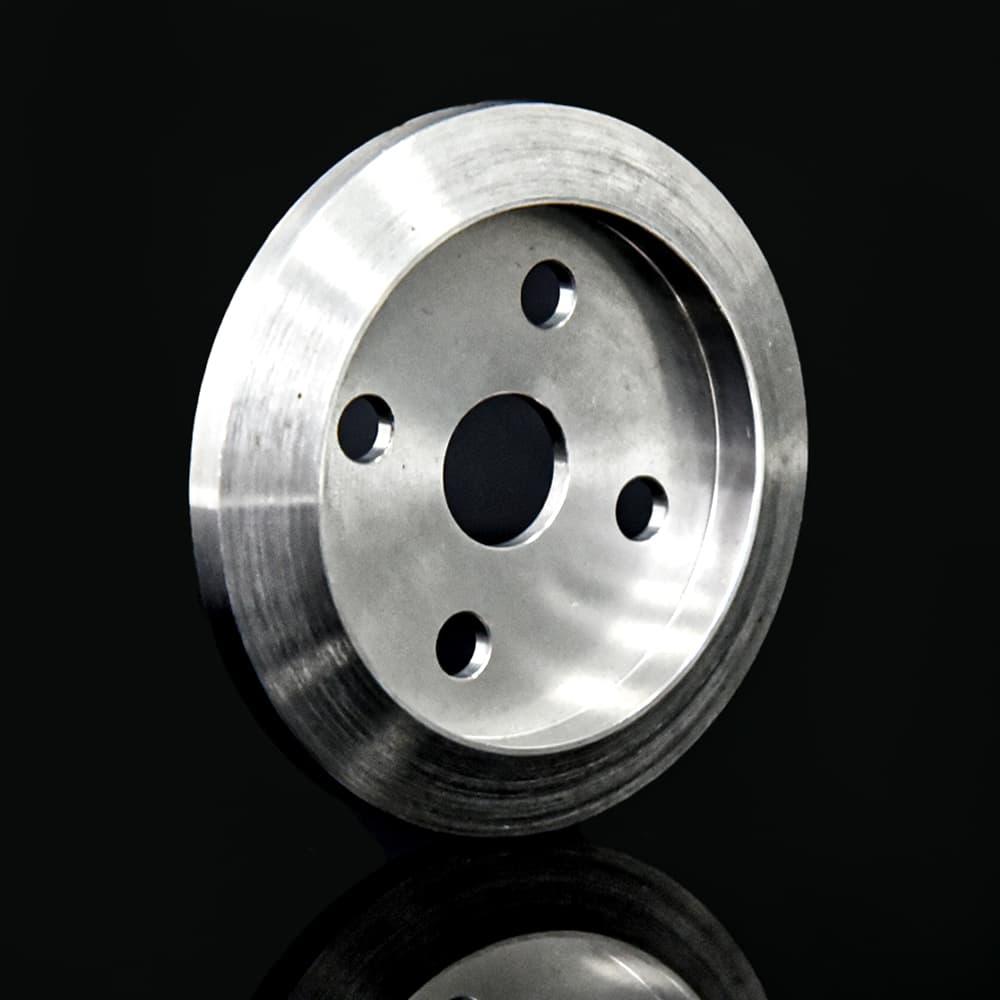

Brushed
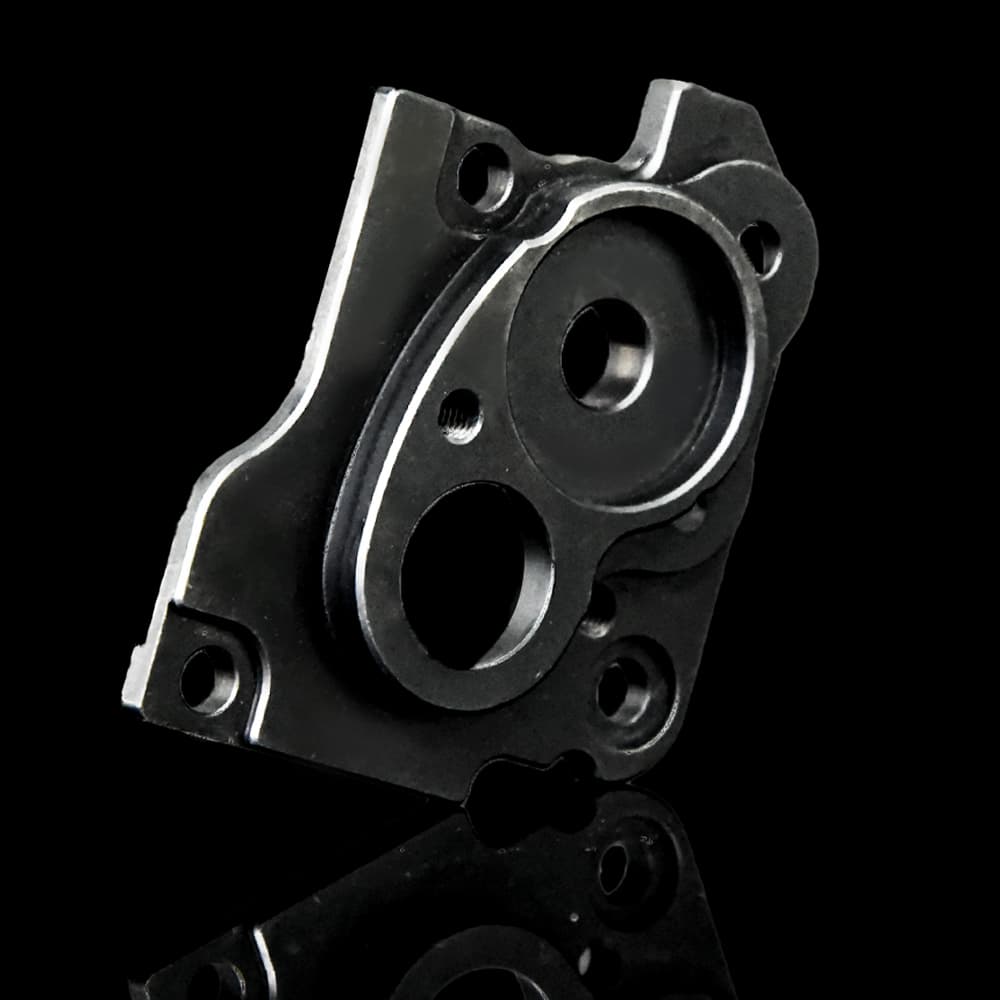

Blackened
| Finishes Option | Finishes Description | Finishes Color | Finishes Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Default Surface | This is the surface finish that results directly from the machining process without any post-processing. It may have visible tool marks and is not typically very smooth. | Various (depends on material) | Basic finish, cost-effective |
| As machined | Parts are machined and deburred, sharp edges are chamfered. Visible machining marks, light surface scratches. | Various (depends on material) | Machining Decorative Patterns |
| Polishing | Polishing refers to a process using mechanical, chemical or electrochemical effects to reduce the surface roughness of the workpiece to obtain a bright and smooth surface. | Various (depends on material) | Improve the smoothness of the workpiece surface |
| Mirror Polishing | A surface finishing process that uses a series of increasingly fine abrasive tools and compounds to produce a highly reflective, mirror-like surface finish. | Various (depends on material) | Improve material aesthetics, ease of cleaning, corrosion resistance, optical reflectivity |
| Bead Blasting | A cold working process to improve fatigue life by bombarding the surface with spherical media. | None (textured surface) | Improve fatigue life, enhance surface strength |
| Sand Blasting | A surface treatment process using compressed air to propel abrasive material against a surface for cleaning or roughening. | None (textured surface) | Clean surface, increase roughness |
| Black Oxide | A conversion coating process to blacken ferrous metals and provide corrosion resistance. | Black | Provide decorative effect, enhance corrosion resistance |
| Passivation | A chemical process to remove iron from the surface of metal and improve corrosion resistance. | None (smooth surface) | Improve corrosion resistance, increase smoothness |
| Phosphating | A chemical conversion coating process to improve corrosion resistance and promote paint adhesion on steel surfaces. | Gray | Provide protection, promote paint adhesion |
| Electrophoretic | A coating technology that applies an organic or inorganic coating to a metal surface through an electrochemical process. | Various (including black white, red, green, champagne, blue) | Provide decorative effect, improve corrosion resistance |
| Electroplating | Electrochemical deposition of a metal coating onto the surface of a part to improve appearance and resistance to corrosion. | Various (depends on plating material) | Improve appearance, increase corrosion resistance |
| Electropolishing | Electrochemical polishing to smooth the surface, improving brightness and reducing roughness. | Mirror finish | Improve smoothness, enhance brightness |
| Chrome Plating | Applying a layer of chromium to a metal part to increase wear and corrosion resistance. | Silver | Improve wear and corrosion resistance |
| Nickel Plating | Applying a layer of nickel to a metal part to improve corrosion resistance and appearance. | Silver | Improve corrosion resistance, enhance appearance |
| Tin Plating | Applying a layer of tin to a metal part, often used to prevent oxidation and improve solderability. | Silver | Prevent oxidation, improve solderability |
| Zinc Plating | Applying a layer of zinc to a metal part to improve corrosion resistance. | Silver | Improve corrosion resistance |
| PVD | Physical vapor deposition (PVD) process that creates a thin film on the metal surface to improve wear and corrosion resistance. | Various colors | Improve wear and corrosion resistance |
| DLC Coating | Diamond-like carbon (DLC) coating that enhances the hardness and wear resistance of the metal surface. | Black | Improve hardness and wear resistance |
| Powder Coating | Applying a powder coating using electrostatic spray and then curing it at high temperatures to form a hard protective layer. | Various (depends on powder color) | Provide protective coating, improve appearance |
| Painting | Applying paint to the metal surface in one or more layers to provide protection and decoration. | Various (depends on paint color) | Provide protective and decorative coating |
| Heat Treatment | Using heat to alter the physical and mechanical properties of the metal. | None (depends on material) | Improve hardness, strength, and durability |
| Laser Marking | Using a laser to mark the metal surface, providing permanent identification. | Various (depends on material) | Provide permanent identification |
| Cleaning | Using various methods to clean the metal surface, removing contaminants and impurities. | None (depends on material) | Remove contaminants, improve surface quality |
CNC Steel Parts Case Study
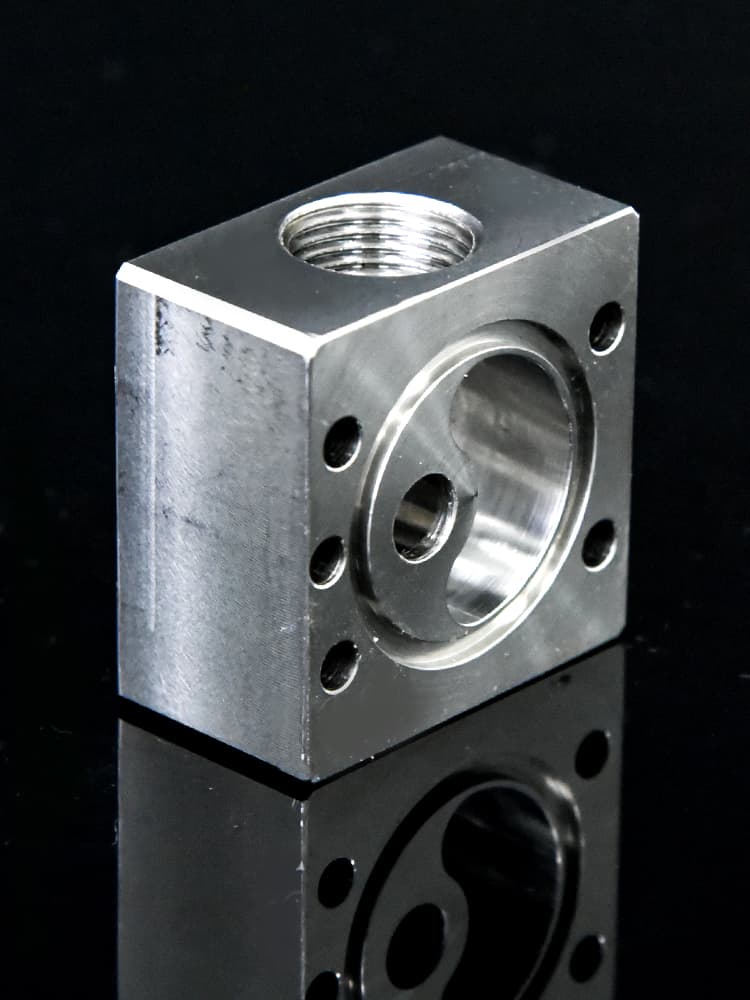
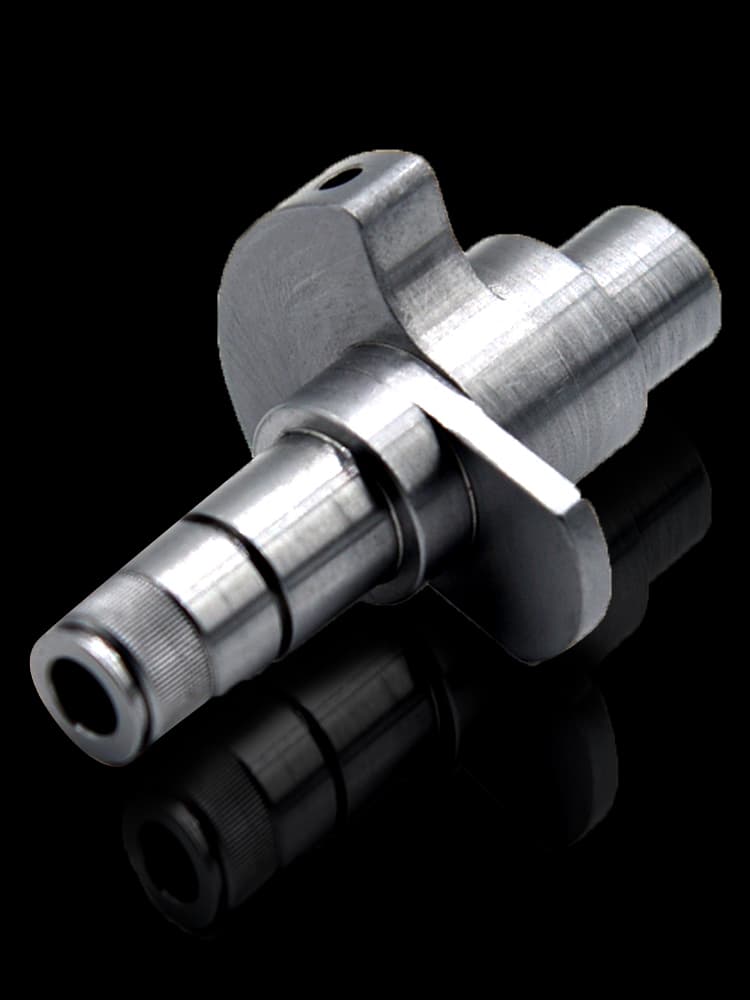
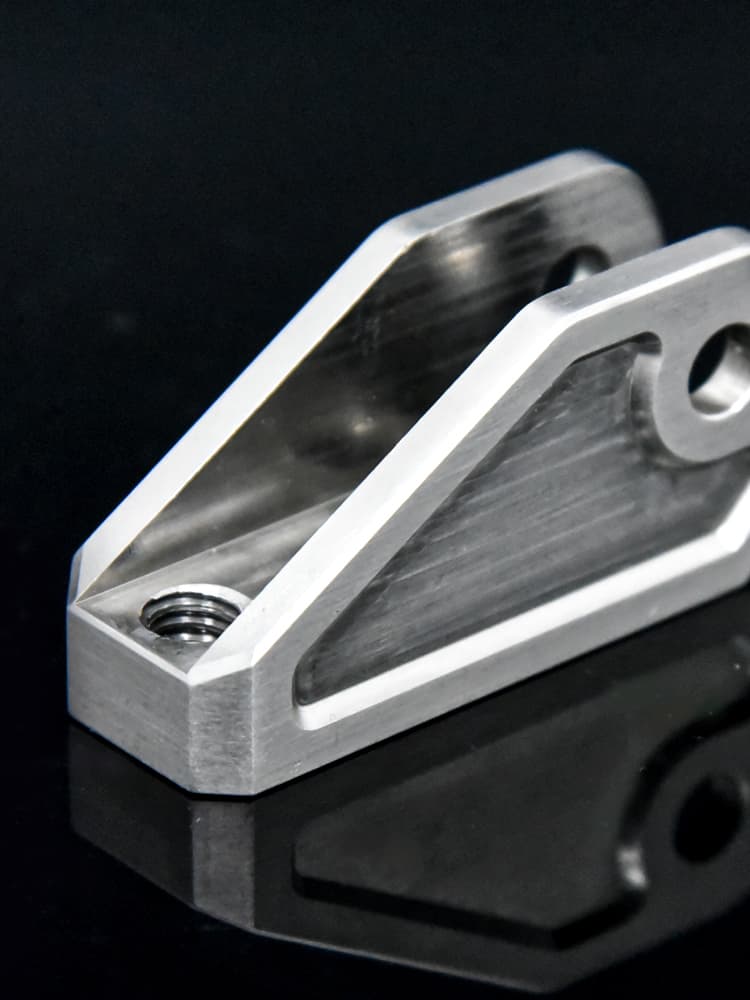
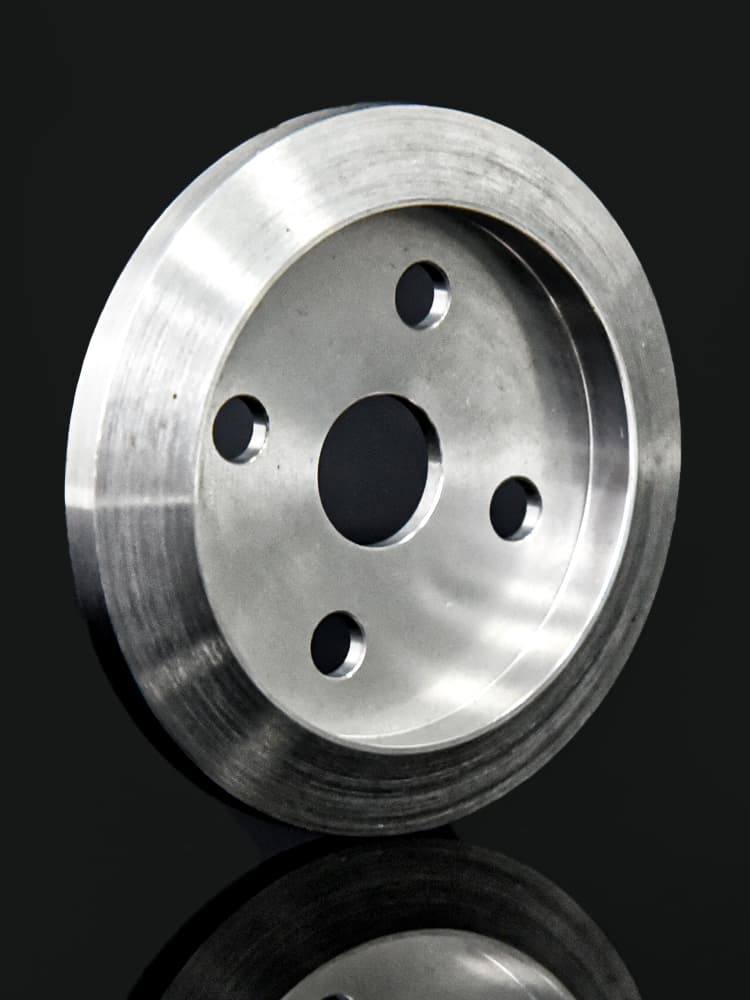
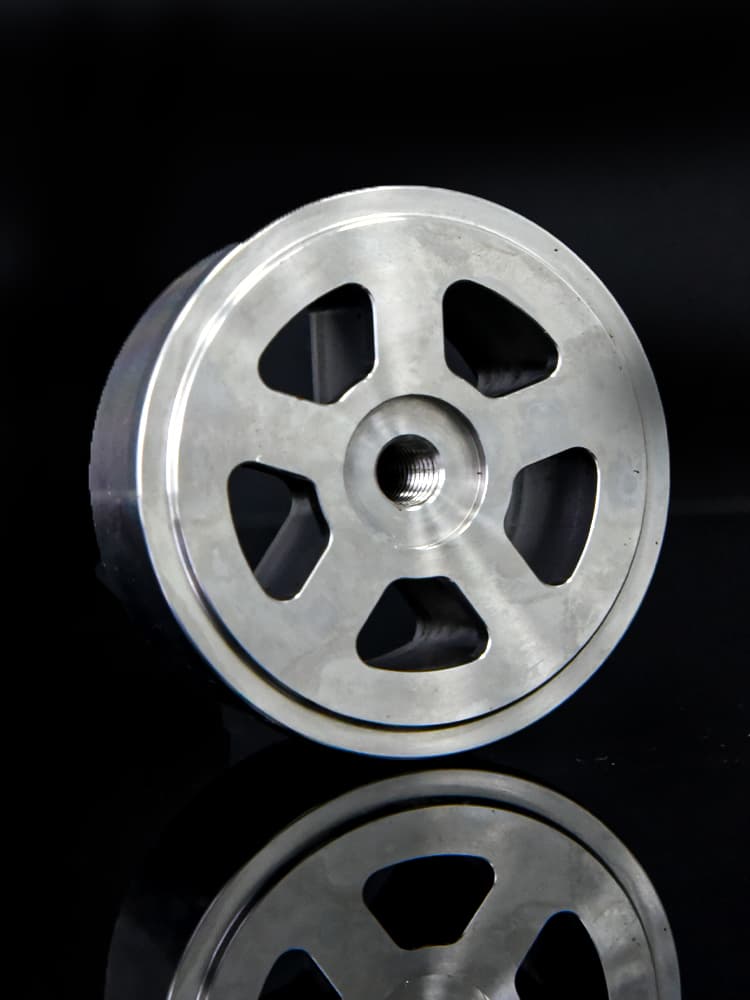
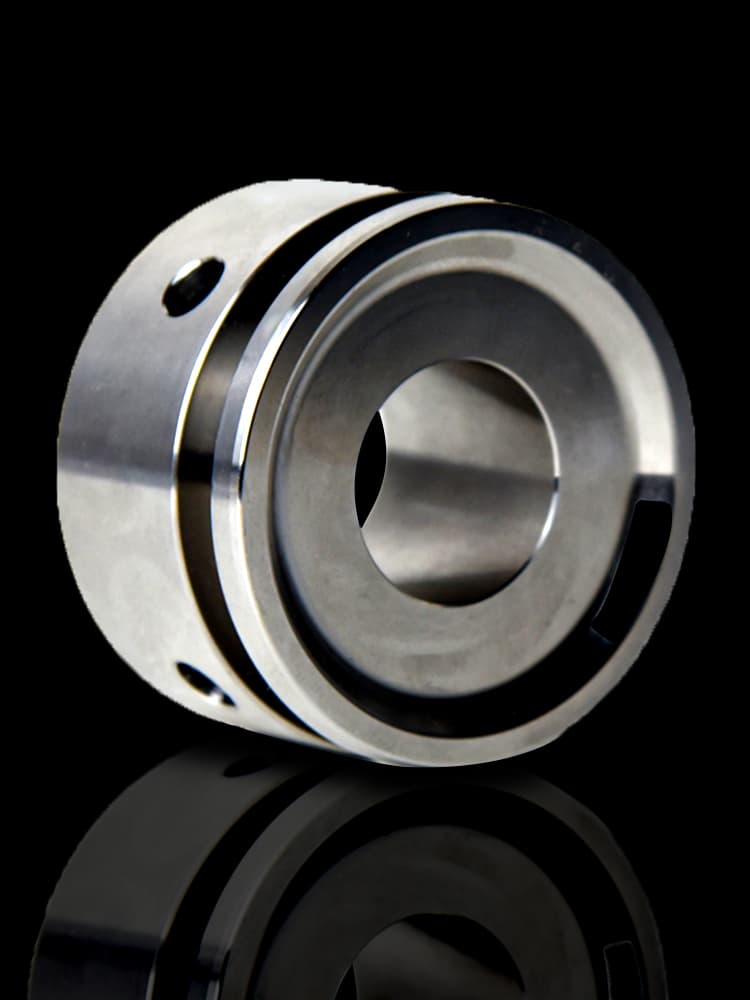
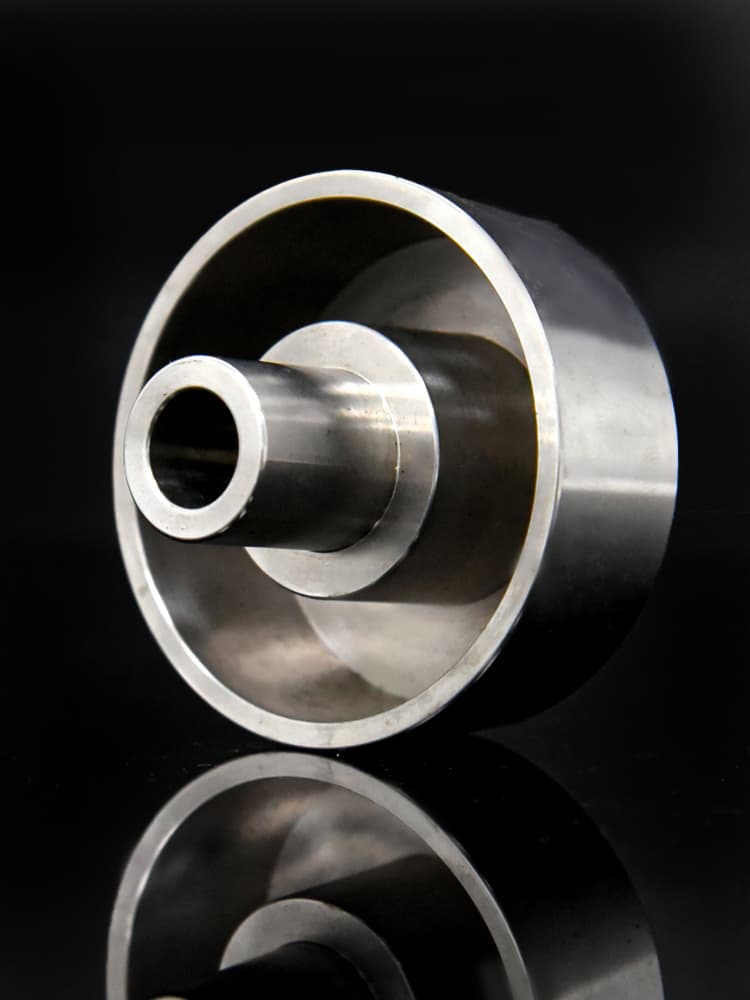
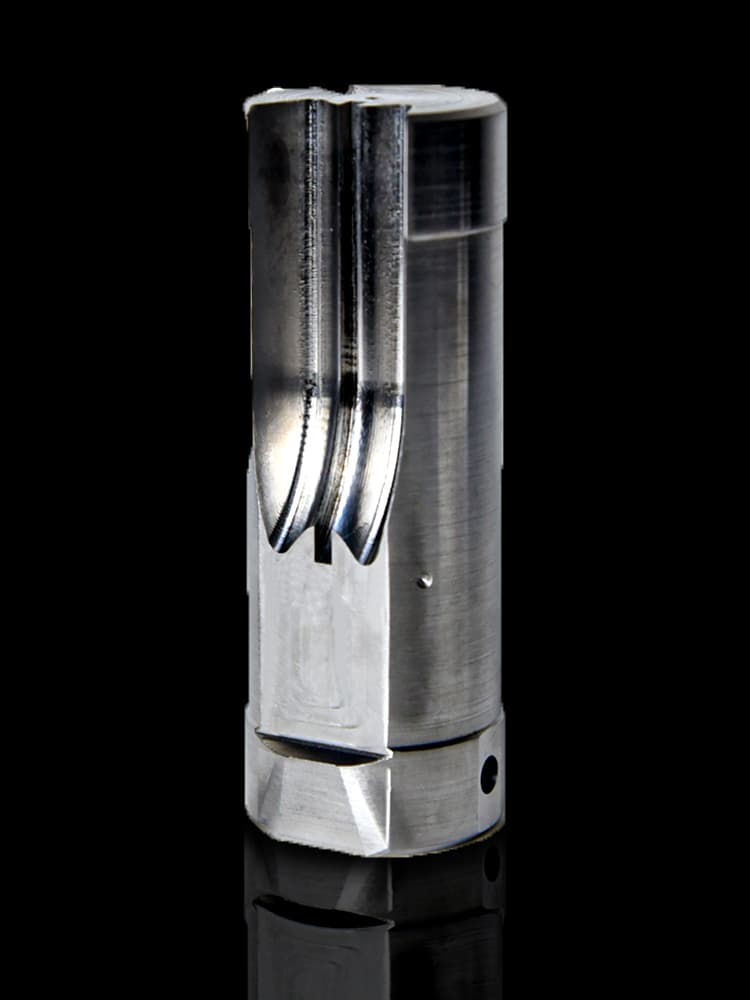
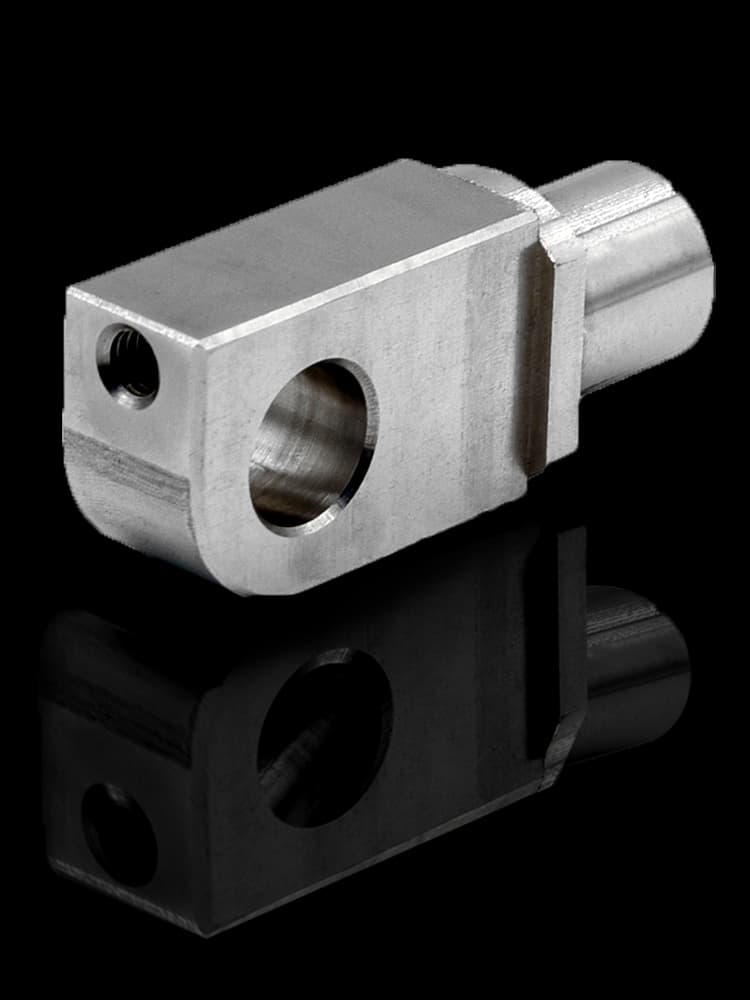
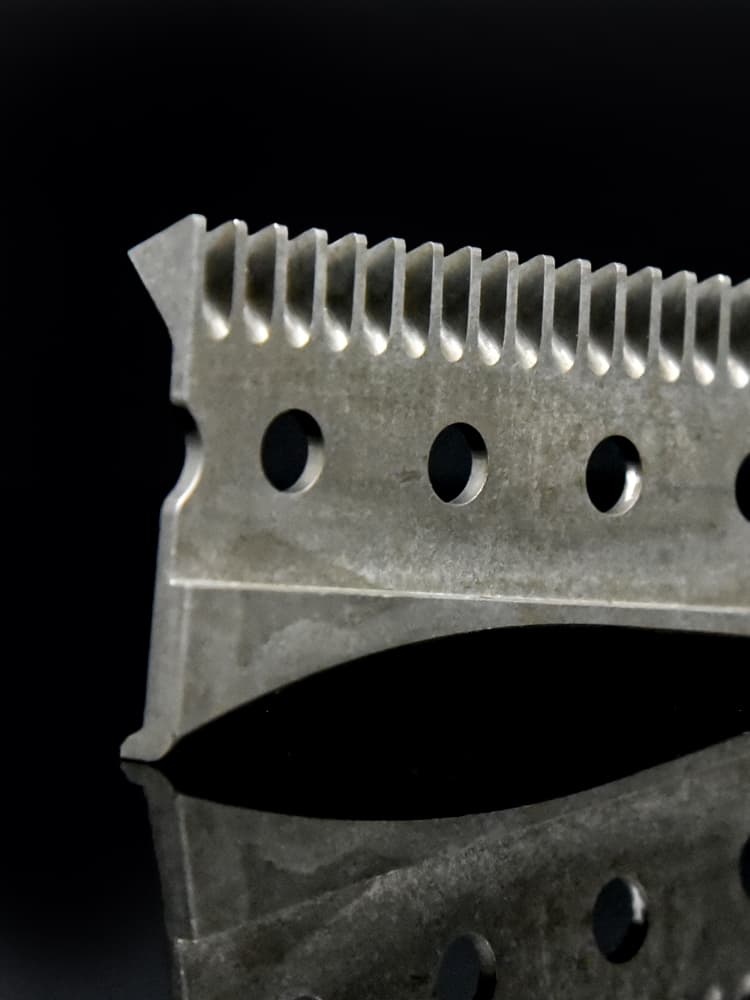










How to Process Custom Steel Parts?
01
Upload drawing
02
DFM Evaluation & Quote

03
Order Confirmtion & Production
04
Quality Inspection & Delivery