For CNC machining parts, the drawing design of the parts should be combined with CNC process features as far as possible in the design stage, and efforts should be made to reduce the processing cost of the parts while taking into account the processing time and quality, here are a few universal optimization design ideas to reduce cnc milling cost:
- Reduce the accuracy tolerance requirements of the parts
The higher the accuracy requirements of the parts, the higher the requirements for equipment and process coordination, which leads to an exponential increase in processing costs.
DFM optimization suggestions:
- assembly parts through the design of surplus and simplify the assembly relationship so as to reduce tolerance requirements
- the use of point lines and planes instead of plane and plane fit to meet the lower tolerance design
- precision and surface requirements are not high parts, avoid high tolerance marking
- Do not designed to machine the surface that does not need machining surface
- Wall thickness of parts using CNC turning and milling, metal parts with wall thickness less than 0.5mm or plastic partswith wall thickness less than 1.0mm, often require special tooling or use more precise equipment such as turning and milling instead of processing, thus significantly increasing labor and replacement costs.
DMF optimization recommendations:
- metal parts with wall thickness greater than 0.5mm
- plastic parts with wall thickness greater than 1.0mm
- try to increase the wall thickness of the parts. Do not design holes in thin walls unless necessary.
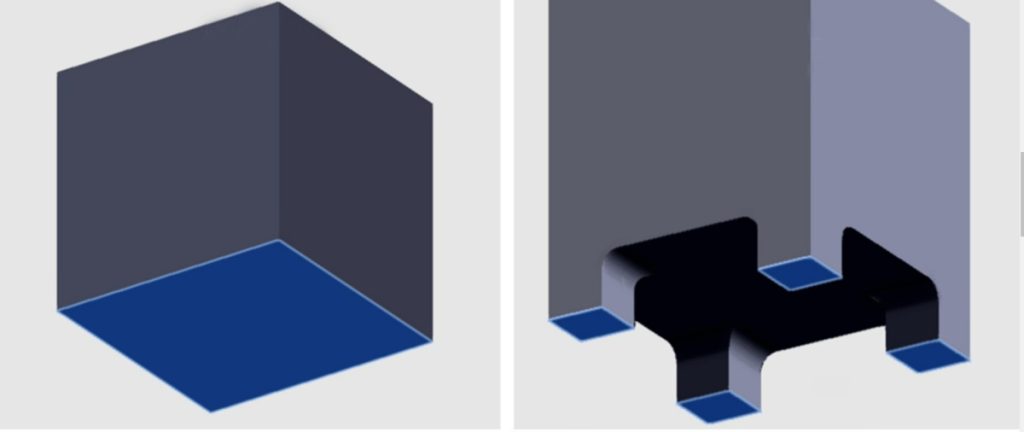
- Reduce the machining area of the part.When the part has high requirements for the flatness (parallelism) of the entire surface, you can refer to the cam structure as shown in Figure 2 to optimize the design (Figure 2 the flatness of the bottom surface of the part requires ± 0.01mm) to reduce the machining area to achieve cost reduction.
DFM optimization recommendations.
- Pre-optimization design: the whole face of the part bottom surface needs to be milled and pinned
- Post-optimization design: Milling pins only for four tabs, effectively reducing the machining area by 75%.
4. External edges of the part machined with C angle instead of R angle. If the external edges of the part need machined to be round , in addition to the need for secondary clamping shovel tooth milling cutter for processing (increased labor costs), the unit travel time of the rounded angle is also longer than the beveled angle. The external edges of the parts are replaced by beveled edges
5. The internal corners of the parts reserved R angle surplus with a sink recessed structure of the internal corners of the parts should be reserved as far as possible rounded assembly surplus, and R angle radius should be directly consistent with the milling cutter. the part in the design (before optimization), due to the lack of R angle assembly surplus, which can not be formed in one go by milling pin, but need to use the more expensive EDM processing 6. Depth to width ratio less than 3:1Milling pin processing area should not be too deep, design the part to reasonably control the depth to width ratio within 3:1, can effectively avoid the hidden cost of possible breakage caused by the longer force surface of the milling cutter.

